How Does a Cpu Read a Hard Drive
The hard bulldoze stores the computer's operating system and individual applications internally, so that they do non have to be loaded from discs each time the figurer is started. These applications are accessed from the drive and pulled to RAM when needed. Saved files are besides stored here, or on external drives for mobility. Difficult drive storage is slower, merely cheaper, than RAM.
Hard Drive Performance
To measure the operation of a bulldoze, we utilise two main characteristics: data charge per unit and seek time. Data rate is the bytes per second that the drive can evangelize to the CPU. Seek time is the time it takes for the difficult drive to commencement sending the commencement byte of information following the initial request from the CPU.
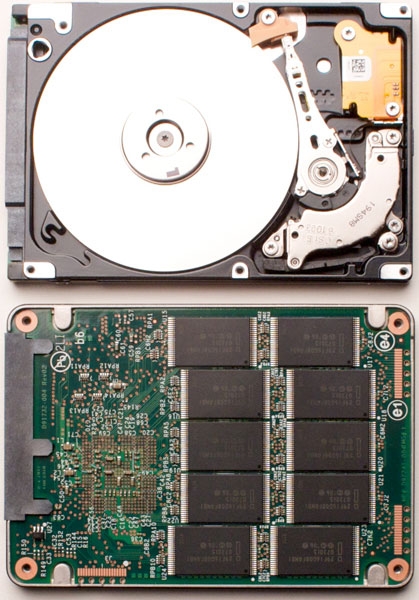
Difficult drives incorporate two important pieces of equipment that allow them to role efficiently as primary data storage. This commencement slice is a magnetic recording medium layered on a loftier-precision glass or aluminum disk, called the "platter." The second slice is called a "caput," and is used to read and write information on the platter. There are two heads per platter, ane on each side, and nigh difficult drives have multiple platters. An internal motor spins the platters, assuasive the heads to read the magnetically stored data.
Solid-state drives (SSDs) utilize solid-state memory that emulates a hard disk interface to store information. SSDs have no moving parts, making them more durable and quieter than hard disk drives.
Hard drives besides have a component called the cache. If information stored in the enshroud is requested, it tin be read directly from the cache rather than searching and reading data from the deejay itself.
Storing the Information
Data is stored on the surface of the platter using organizational elements known equally sectors and tracks. Tracks are concentric circles that surround the unabridged platter. Sectors are wedges that, when grouped together, course a rails. Sectors contain a fixed number of bytes – normally 256 or 512 – and are grouped into clusters.
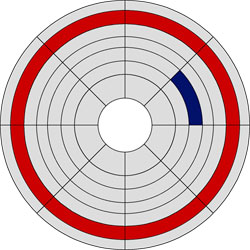
Reddish: Rail; Bluish: Sector
Before a drive tin be used, information technology must be properly formatted. A low-level format is performed that establishes the tracks and sectors on the platter to prepare the disk to hold blocks of bytes. After the low-level formatting, a high-level format is performed to gear up the disc to hold files. The high-level format writes disc important structures for the operating organization to the disc.
Hard Bulldoze Interfaces
Historical: Integrated Bulldoze Electronics (IDE)
IDE was used in PCs for about 20 years, and is being phased out. It is besides referred to every bit AT Attachment (ATA) or Parallel ATA (PATA). IDE controllers accept 2 channels, and each channel is a shared autobus – only one bulldoze can talk at a fourth dimension and the drives can merely talk to the controller. IDE express computers to 4 drives without an expansion card, and is only for drives internal to the computer.
Modest Computer Organisation Interface (SCSI)
In 1986, some other interface standard was developed, called SCSI, using a more intelligent and complicated controller to manage the bus. Up to 15 devices can be continued to a SCSI autobus and some have dual controllers. Using SCSI will typically require an add-in carte du jour. Tape drives, scanners, and the beginning CD-ROM drives were designed for SCSI. Like IDE, only one device can talk on a SCSI bus at a time, but devices tin can talk directly to each other also equally to the controller.
Serial ATA (SATA)
SATA is the evolution of IDE. Adapters are available for use betwixt the two, but they are non backwards-compatible. SATA uses a direct serial connexion betwixt the motherboard and each drive, which gives smaller/narrower connectors and cables and faster speeds than IDE. The latest version, SATA 2, airtight the speed gap with SCSI and kept the low price of IDE.
Hard Drive Configuration
Redundant Array of Contained Disks (RAID: Configuration)
RAID refers to a scheme, non an interface, of using multiple hard drives to create one or more than logical units to gain mistake tolerance or increased chapters. Historically, RAID was used exclusively in expensive server hardware, but is at present affordable enough for personal desktops. There is hardware and software RAID, and they may be used with IDE, SCSI, or SATA hard drives.
Source: https://e115.engr.ncsu.edu/hardware/hard-drive/
0 Response to "How Does a Cpu Read a Hard Drive"
Post a Comment